Fire Factor
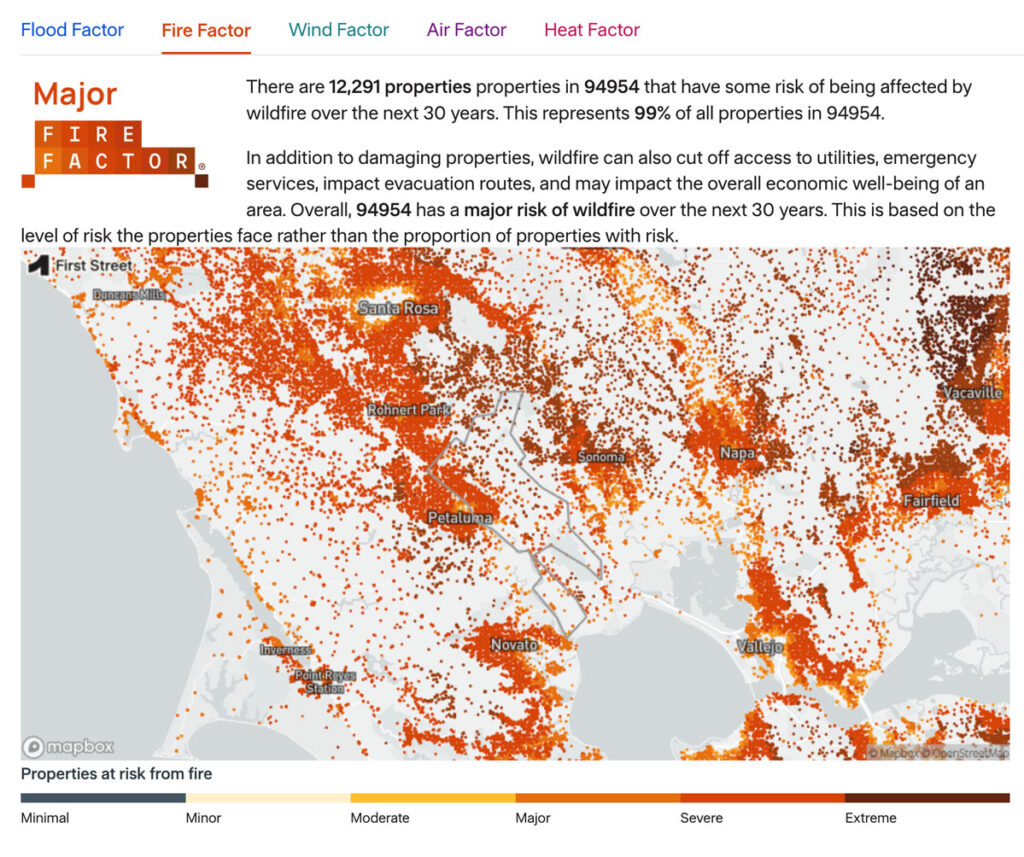
As part of the Pyregence Consortium, Spatial Informatics Group partnered with the risk analysis firm First Street Foundation to create a property-level wildfire risk model for every property in the conterminous United States. The First Street Foundation Wildfire Model (FSF-WFM) is the first national, climate-adjusted, property-specific wildfire risk assessment in America. FSF-WFM informs Fire Factor, First Street Foundation’s fire risk data product.
BehavePlus 7
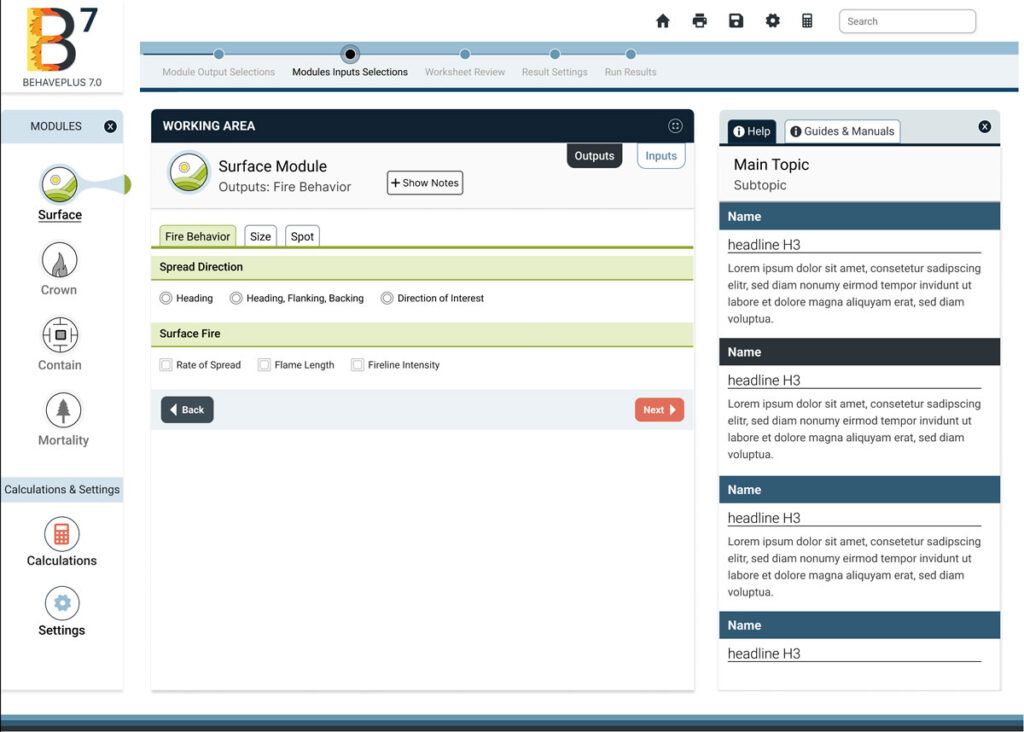
BehavePlus 7 is a desktop app that predicts fire behavior and environment using models. It simulates fire spread rate, spotting distance, scorch height, tree mortality, fuel moisture, wind speed effects, and more.
PyreCast
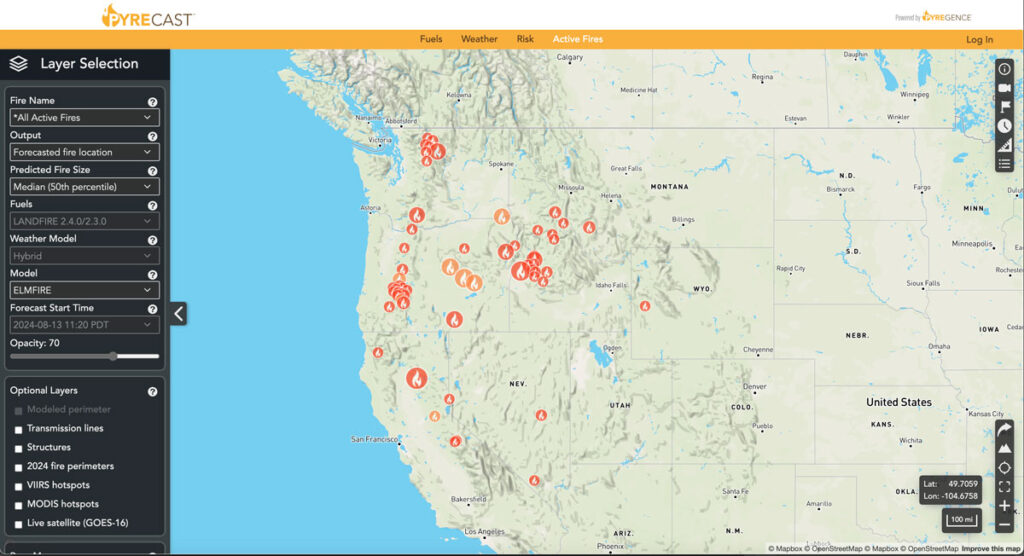
PyreCast empowers agencies and individuals to make decisions regarding evacuation orders, suppression and containment strategies, power grid shut-offs, and more by providing them with near real-time fire updates, fire spread forecasts, and fire risk assessments.
Planscape
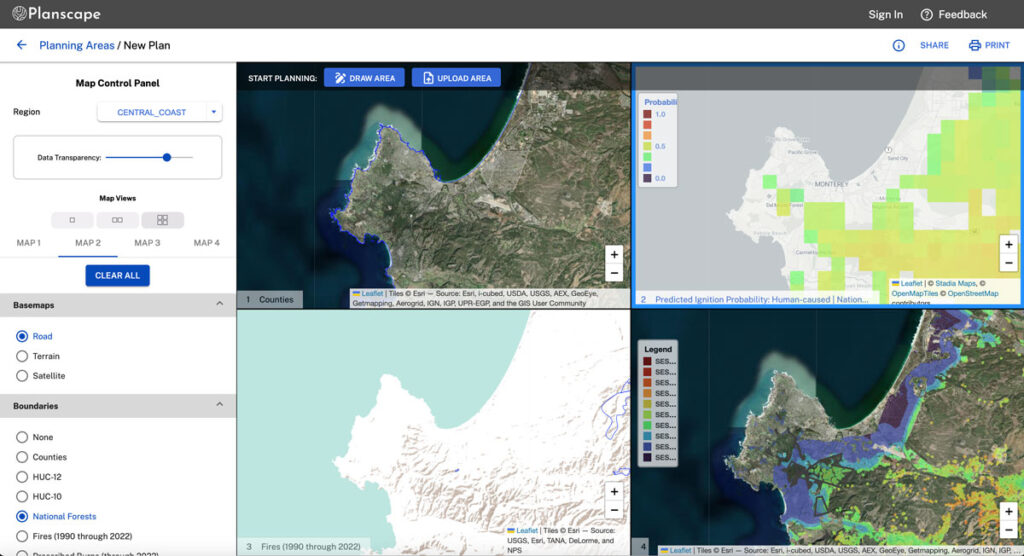
Planscape is a free decision support tool built to maximize wildfire resilience and ecological benefits across the State of California.
Planscape helps regional planners prioritize landscape treatments to mitigate fire risk, maximize ecological benefits and help California’s landscapes adapt to climate change
Planscape is a collaborative effort by the California Natural Resources Agency and US Forest Service, The University of California, and Spatial Informatics Group (SIG) with support from Google.org.
Eastern Sierra Climate & Community Resilience Project

the USDA Forest Service, specifically the Inyo National Forest, along with numerous state and local governments and NGOs. SIG was hired to assist with ESCCRP because of our scientific and operational experience and expertise in fire modeling, land restoration, and maintenance.
Monitoring Severely Burned Redwood Forest

Save the Redwoods turned to Spatial Informatics Group (SIG) for their expertise in data collection, wildfire modeling, and remote sensing. SIG created a post-fire monitoring plan to quantify the fire’s effects and track recovery after the CZU Lightning Complex fires.
Assessing Extreme Fire Risk In California

Some California fires were ignited by power lines and communication facilities downed by Santa Ana winds. In response, the California Public Utilities Commission needed accurate fire threat maps to address ignition dangers from electrical infrastructure.
Planning And Implementing Fuel Treatments To Reduce Fire Hazard And Restore Healthy Wildlands And Forest Communities

California landowners, land managers, and planners are acutely aware of their region’s exposure to wildfire and its associated hazards. Local, state, and federal efforts to moderate fire behavior with fuel treatments have dramatically expanded as wildfires have increased in size, severity, and community impacts.
