Close
Close
SIG’s Forest Carbon Analysis Tool (FCAT) identifies the greenhouse gas mitigation potential of fuel treatments on forestlands. The tool facilitates the assessment of emission profiles associated with various treatments by running spatial simulations of forest growth and yield, wildfire, and wildfire effects.
FCAT automates the entire REM forecast methodology within a single command line prompt
Spatial Informatics Group and its partners needed a way to model carbon mitigation impacts in forestlands. So we built FCAT. This system automates SIG’s open science Reduced Emissions from Megafires methodology to quantify and monetize carbon emissions avoided through forest treatments that reduce the severity and scope of wildfires.
FCAT is able to simulate virtually any disturbance, management regime, or fuels treatment at any point in the future. With every timestep, FCAT provides data on carbon, forest stand structure, fire behavior, fire effects, and emissions in both treatment and control conditions.
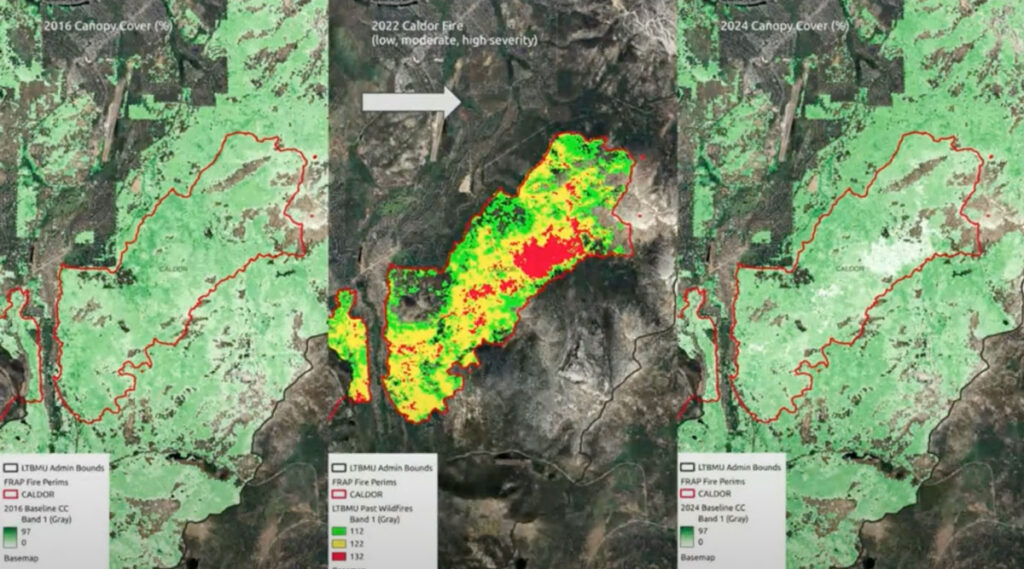
FCAT’s components use pixel-based measurements of vegetation type, structure, and other factors to conduct forest growth, carbon flux, and fire spread simulations. This architecture allows FCAT to simulate large landscapes by automating primary Forest Service tools like the Forest Vegetation Simulator, accomplishing in days what previously took months.
The tool makes use of third party components, including LANDFIRE, from the US Departments of Agriculture and Interior, which derives wildland fuel loading and structure from Landsat data, and Treemap, from the USDA Forest Service, which is a comprehensive forest inventory and structure database covering the entire conterminous United States. LiDAR data from fixed wing platforms and inputs from the Hansen Global Forest Change database from Landsat multispectral data also contribute to FCAT.
FCAT’s components include GIS processing, Forest Vegetation Simulator modeling (forest growth, fuel treatments, and wildfire), Monte Carlo GridFire simulations, FOFEM smoke emission model estimates, and carbon quantification. FCAT is flexible so that these components can also be used as microservices for projects beyond greenhouse gas mitigation.
As a command line tool, FCAT is primarily used internally by Spatial Informatics Group in service of projects addressing a wide range of client needs. Though originally developed to automate the Reduced Emissions from Megafires modeling process, the tool has been revolutionary for multiple projects and applications.
FCAT is being leveraged in Planscape to facilitate the assessment of impacts associated with various treatments at the landscape level. The Million Acre Strategy uses it to simulate fuel treatments across California. We are using FCAT to generate data for integrated forest management project feasibility for Greenline Climate.
Explore all the possibilities